Security Innovation Smart Contract CTF入门
参考文章
智能合约安全系列文章之反编译篇 opcode逆向基础 关于evm中数据存储 以太坊中智能合约中的存储
这里记录一下安装web3.py的过程,装的头皮发麻,通常肯定是使用命令pip3 install web3,但是我的报错是几个模块安装出错并且visual c++环境没有。
解决过程: 最开始直接下载web3-5.28.0-py3-none-any.whl安装还是报错,这个和用pip3安装没啥区别似乎,后来手动下载web3的包用python setup.py install下载,这个过程可以成功下载一些包,但到最后还会在visual c++报错,然后用VisualCppBuildTools_Full.exe安装环境。最后又试了一下直接用pip3安装,就成功了。可能需要的包在前面都装好了吧。
Lock Box
考点:合约反汇编,EVM 中 storage 存储的读取。太菜了,这题确实不会,第一次了解到了EVM的反汇编知识,学到了很多知识。这里也认真的分析一遍合约反汇编代码。
合约源码,源码比较容易看懂,主要就是满足pin == _pin,但这里肯定无法猜出来。但这里可以看到pin的初始定义用了uint256 private pin;。这告诉我们这个值是储存在storage中的,那我们如果可以知道它在storage上的地址就能够通过合约交互获取到它的值了
EVM里有三种存储方式:
- stack “PUSH”命令
- memory 用“MSTORE”指令
- stroage 用“SSTORE”指令存储数据,类似于存储在硬盘上,最耗费gas的存储 针对这三种存储方式,展开又有一些内容了
pragma solidity 0.4.24;
contract CtfFramework{
event Transaction(address indexed player);
mapping(address => bool) internal authorizedToPlay;
constructor(address _ctfLauncher, address _player) public {
authorizedToPlay[_ctfLauncher] = true;
authorizedToPlay[_player] = true;
}
modifier ctf() {
require(authorizedToPlay[msg.sender], "Your wallet or contract is not authorized to play this challenge. You must first add this address via the ctf_challenge_add_authorized_sender(...) function.");
emit Transaction(msg.sender);
_;
}
// Add an authorized contract address to play this game
function ctf_challenge_add_authorized_sender(address _addr) external ctf{
authorizedToPlay[_addr] = true;
}
pragma solidity 0.4.24;
contract Lockbox1{
uint256 private pin;
constructor(address _ctfLauncher, address _player) public payable
{
pin = now%10000;
}
function unlock(uint256 _pin) external{
require(pin == _pin, "Incorrect PIN");
msg.sender.transfer(address(this).balance);
}
}首先是main函数的反汇编代码。对于memory[0x40:0x60] = 0x80;这个几乎每个合约的前几个操作码,对应的opcode如下,简单讲就是把0x80 写到[0x40 ,0x40 + 0x20] 这块内存里面,因为内存是空的,这会创建新的内存,分配了32字节的内存空间。不过其实后续也不太会用到只是了解一下吧。
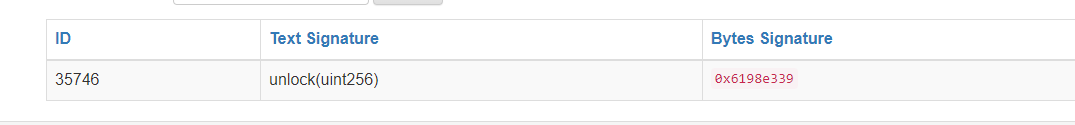
下面的0x3c3e1662也是可以通过签名网站查到的,不过也就限于一些常见的函数名字。

关于opcode操作的分析还是先放一放吧。。。先把反汇编代码看懂
contract Contract {
function main() {
#进入main函数,把0x80写到[0x40 ,0x40 + 0x20]这块内存里面,因为内存是空的,这会创建新的内存
#对应的opcode操作
#PUSH1 0x80
#PUSH1 0x40
#MSTORE 即为 MSTORE(arg0, arg1)从栈中获取两个参数,表示MEM[0x40:(0x40+32)=0x60] = 0x80。
#正在做的是分配96个字节的存储器并将指针移动到第64个字节的开头。 我们现在有64个字节用于临时空间,32个字节用于临时存储器存储。
#可靠性文档声明如下:"Solidity以一种非常简单的方式管理内存:内存中位置0x40有一个"空闲内存指针"。如果你想分配内存,只需使用该点的内存并相应地更新指针。"
memory[0x40:0x60] = 0x80;
#判断用户输入的data内容长度是否小于4,如果满足就revert(关于revert,assert,require的比较)
if (msg.data.length < 0x04) { revert(memory[0x00:0x00]); }
#与上0xffffffff(即四字节)获取data的低4位,赋值给var0
var var0 = msg.data[0x00:0x20] / 0x0100000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 & 0xffffffff;
#这里的0x3c3e1662代表的是函数进行sha3加密后的前四位。所以就是判断是否调用这个函数()
if (var0 == 0x3c3e1662) {
// Dispatch table entry for ctf_challenge_add_authorized_sender(address)
var var1 = msg.value;
#判断var1是否存在
if (var1) { revert(memory[0x00:0x00]); }
#var1赋值为0x0092
var1 = 0x0092;
#传入的参数,并且与0xffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffff,说明低位20bytes数值保留,高位12bytes数值置0。这应该是address数据
#并且这里0x04前面四个字节是赋值给了var0的,所以从0x04开始取
var var2 = msg.data[0x04:0x24] & 0xffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffff;
#调用函数并且传入参数
ctf_challenge_add_authorized_sender(var2);
stop();
#如果调用的是另一个函数,这里也可以搜到到 unlock(uint256)函数名,下面的操作是一样的
} else if (var0 == 0x6198e339) {
// Dispatch table entry for unlock(uint256)
var1 = msg.value;
if (var1) { revert(memory[0x00:0x00]); }
var1 = 0x00bf;
var2 = msg.data[0x04:0x24];
unlock(var2);
stop();
} else { revert(memory[0x00:0x00]); }
}然后是两个函数,这里重点看unlock函数
function unlock(var arg0) {
#将msg.sender 放在0x00:0x20 的32字节内存中
memory[0x00:0x20] = msg.sender;
#0x20:0x40 赋值为0x00
memory[0x20:0x40] = 0x00;
#if里面首先通过keccak256(memory[0x00:0x40])加密了0x00:0x40的内容,获取了低位的一个字节的内容。这里可以推测出是一个bool类型数据。所以这里所取得数据其实对应源码里面得这一行代码mapping(address => bool) internal authorizedToPlay;
#storage[keccak256(memory[0x00:0x40])]等同于authorizedToPlay[msg.sender]
if (storage[keccak256(memory[0x00:0x40])] & 0xff) {
var temp0 = memory[0x40:0x60];
log(memory[temp0:temp0 + memory[0x40:0x60] - temp0], [0xf0c55d049e61d6dcd81c1f2715f135c87551e981a34759c240851595cfcb38c7, msg.sender]);
#if判断storage[0x01]中0x01插槽存储的内容是否和arg0相等,这里也可以推测这个插槽中存储的就是pin的值
if (storage[0x01] == arg0) {
var temp1 = address(this).balance;
var temp2 = memory[0x40:0x60];
var temp3;
#这里进行了转账操作,更加确定了推测
temp3, memory[temp2:temp2 + 0x00] = address(msg.sender).call.gas(!temp1 * 0x08fc).value(temp1)(memory[temp2:temp2 + memory[0x40:0x60] - temp2]);
var var0 = !temp3;
#是否转账成功
if (!var0) { return; }
var temp4 = returndata.length;
memory[0x00:0x00 + temp4] = returndata[0x00:0x00 + temp4];
revert(memory[0x00:0x00 + returndata.length]);
} else {
var temp5 = memory[0x40:0x60];
memory[temp5:temp5 + 0x20] = 0x08c379a000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000;
var temp6 = temp5 + 0x04;
var temp7 = temp6 + 0x20;
memory[temp6:temp6 + 0x20] = temp7 - temp6;
memory[temp7:temp7 + 0x20] = 0x0d;
var temp8 = temp7 + 0x20;
memory[temp8:temp8 + 0x20] = 0x496e636f72726563742050494e00000000000000000000000000000000000000;
var temp9 = memory[0x40:0x60];
revert(memory[temp9:temp9 + (temp8 + 0x20) - temp9]);
}
} else {
var temp10 = memory[0x40:0x60];
memory[temp10:temp10 + 0x20] = 0x08c379a000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000;
var temp11 = temp10 + 0x04;
var temp12 = temp11 + 0x20;
memory[temp11:temp11 + 0x20] = temp12 - temp11;
memory[temp12:temp12 + 0x20] = 0x9c;
var temp13 = temp12 + 0x20;
memory[temp13:temp13 + 0x9c] = code[0x03c2:0x045e];
var temp14 = memory[0x40:0x60];
revert(memory[temp14:temp14 + (temp13 + 0xa0) - temp14]);
}
}
}
直接在控制台交互就行了。
PiggyBank challenge
考点:CharliesPiggyBank合约重写collectFunds没有使用onlyOwner修饰符,导致不是owner也能调用withdraw从而转移amount。还是考察的一些基础语法知识。考点很简单没啥好说的,这题也没看wp就做出来了。
合约源码如下。简单分析一下,本菜鸡在看完一些基础语法之后也能看懂了。
在PiggyBank合约中核心点在于collectFunds方法中,调用了withdraw方法来像调用者账户发送币,但是这里用onlyOwner修饰限制了调用者必须是合约拥有者,再看另外一个合约CharliesPiggyBank,重写了collectFunds方法,但是可以看到用了public修饰为公共方法,并且没有onlyOwner限制。很显然,这里就存在漏洞了,我们直接调用这个函数就行了。
contract PiggyBank{
using SafeMath for uint256;
uint256 public piggyBalance;
string public name;
address public owner;
constructor(address _ctfLauncher, address _player, string _name) public payable
{
name=_name;
owner=msg.sender;
piggyBalance=piggyBalance.add(msg.value);
}
function() external payable{
piggyBalance=piggyBalance.add(msg.value);
}
modifier onlyOwner(){
require(msg.sender == owner, "Unauthorized: Not Owner");
_;
}
function withdraw(uint256 amount) internal{
piggyBalance = piggyBalance.sub(amount);
msg.sender.transfer(amount);
}
function collectFunds(uint256 amount) public onlyOwner{
require(amount<=piggyBalance, "Insufficient Funds in Contract");
withdraw(amount);
}
}
contract CharliesPiggyBank is PiggyBank{
uint256 public withdrawlCount;
constructor(address _ctfLauncher, address _player) public payable PiggyBank(_ctfLauncher, _player, "Charlie")
{
withdrawlCount = 0;
}
function collectFunds(uint256 amount) public{
require(amount<=piggyBalance, "Insufficient Funds in Contract");
withdrawlCount = withdrawlCount.add(1);
withdraw(amount);
}
}SI
合约源码
contract SIToken is StandardToken {
using SafeMath for uint256;
string public name = "SIToken";
string public symbol = "SIT";
uint public decimals = 18;
uint public INITIAL_SUPPLY = 1000 * (10 ** decimals);
constructor() public{
totalSupply_ = INITIAL_SUPPLY;
balances[this] = INITIAL_SUPPLY;
}
}
contract SITokenSale is SIToken {
uint256 public feeAmount;
uint256 public etherCollection;
address public developer;
constructor(address _ctfLauncher, address _player) public payable
{
feeAmount = 10 szabo;
developer = msg.sender;
purchaseTokens(msg.value);
}
function purchaseTokens(uint256 _value) internal{
require(_value > 0, "Cannot Purchase Zero Tokens");
require(_value < balances[this], "Not Enough Tokens Available");
balances[msg.sender] += _value - feeAmount;
balances[this] -= _value;
balances[developer] += feeAmount;
etherCollection += msg.value;
}
function () payable external{
purchaseTokens(msg.value);
}
// Allow users to refund their tokens for half price ;-)
function refundTokens(uint256 _value) external{
require(_value>0, "Cannot Refund Zero Tokens");
transfer(this, _value);
etherCollection -= _value/2;
msg.sender.transfer(_value/2);
}
function withdrawEther() external{
require(msg.sender == developer, "Unauthorized: Not Developer");
require(balances[this] == 0, "Only Allowed Once Sale is Complete");
msg.sender.transfer(etherCollection);
}
}